5 On-Page SEO Mistakes Most E-commerce Website Owners Make

When was the last time you googled a product or a service?
Search engine referral traffic is what marketers crave the most and it is the hardest thing to get. There are hundreds (if not thousands) of similar products and services on the Internet and all of them compete for the high ranking.
With e-commerce, things get even more complicated. An average e-commerce store usually has multiple product pages and product categories, different pages for different countries, an awful lot of redirects, and huge volumes of traffic to handle.
SEO for e-commerce helps online stores remain visible for the crawlers and rank high in search. However, there are some common mistakes that most e-commerce store owners make, and you may be among them as well.
We’ll reveal these pitfalls below and will also provide a way to resolve them. Ready to optimize your store? Let’s start!
#1. Duplicate Content
This is the biggest SEO-related problem that e-commerce stores face. Duplicate content confuses search engine crawlers and leads to a decreased ranking of pages and loss of their value. Here are the most frequent duplicate content issues.
Cross-Category URLs
As mentioned earlier, e-commerce stores have multiple product categories for the same product type. An example would be “Floral dresses” and “Summer dresses”.
This happens most often for marketing reasons and marketers need these categories to existing. But during indexing, Google will not know which of the pages is of top priority and thus, may either ignore them at all or divide the rank between the pages.
There are several ways to battle the cross-category URLs issue:
- 301 redirect
- noindex, nofollow tag
- canonical tag
301 redirect is used to send the users to a URL that is different from the one they entered. I.e., example.com/dresses/summer would be a primary link. Then, you can apply 301 redirects to example.com/dresses/floral-dresses to eliminate duplicate content.
Noindex, nofollow tags are used in order to prevent page indexing. Thus, a search engine will not show the tagged pages in the search results and will not break down the value of the primary page among the duplicates.
The canonical tag is used to show search engines that there is only one main page that should be shown in the search results.
Title Tags
Title tags are needed to help both users and Google understand what the page is about. Therefore, if a few pages have the identical title tag, it will lead to confusion and lower ranking.
Depending on the available resources, you can either algorithmically generate title tags, based on the page’s H1, or use Excel (yes, so simple) and create a template design for manual title tags generation.
Manufacturer’s Description
The items from a manufacturer often come with a ready description. While it may seem time-saving for the marketers to use a ready and available content, it’s actually an SEO mistake that could cost you traffic.
Think about that: manufacturers send their products to a number of stores, and all of them use the same description. In this case, the search engine will rank big stores higher than the ones with a smaller rank.
So take some time to write unique content with relevant keywords. Actually, the overall quality and relevance of the content affect ranking significantly. Read more about the RankBrain and requirements for the content here.
#2. No Image Description
Google can’t recognize an image but needs to know what the image is about. By naming the image correctly, you help search engines recognize it and increase the chances that the image will appear in search results.
Take shoes, for example. If a user enters “red converse shoes buy london” in a search bar and your image has the same or similar name, it will appear in the search results. On the other hand, if you leave the original “IMG0028”, neither Google nor the user will see it.
A note: put the name subject of the photo on the first place in the image description. In the example above, the main subject would be “red converse shoes” so the name can be something like “red-converse-shoes”. As well, keep it simple and readable.
As well, keep in mind the following tips on image optimization for SEO.
Size and Format
The image format is important as various visual elements have different requirements for quality and size. There are a few options to choose from, depending on your goal:
- JPEG: provides bright colours, good clarity, suits well for large photos and illustrations, retains the relatively small size;
- PNG: retains transparent background;
- WebP: similar to JPEG, it has good quality and small image size.
- SVG: suits for logos and icons – in other words, small images that require high quality and small size.
The speed of a site load affects SEO and user experience, we’ll talk about it in detail a bit later. What you need to remember for now is that when you upload heavy images, they will slow down the site load. Thus, adjust the image size to the one that you are going to display. If you plan to display a 300×150 image, don’t upload a 3000×1500 one.
Alt Tags
Alt tag (alt text) is a text that appears when the image cannot be displayed. Say, you turned off the images in your browser and opened a newsletter in your email – an optimized letter would still contain the descriptive information near the image boxes. And, depending on the description, the user will either be interested to learn more or prefer to skip the mysterious “IMG0028”.
When you write an alt tag, keep it descriptive so that the users and search engines know what’s in the image. Also, include keywords in the description, if they are relevant.
A note: use only relevant keywords for both the image description and alt tag. As well, keep it natural. Do not write something like “Women-Pleaser-Shoes-White-Buy-London”. That looks ridiculous and confuses the search engine.
#3. No URL Optimization
URLs not only hold the page’s location but also inform the users and search engines about the page content. Like any page element, URLs have to be optimized in order to make them SEO-friendly and increase page visibility. Here is how to do it:
- Make them readable and clear – a user (and Google) should understand URLs.
- Use hyphens only – no underscores! Google cannot read underscores.
- Include mobile URLs in the site map to help mobile-friendly pages of your site rank higher.
- Add relevant keywords for better search.
And don’t forget about the redirects and canonical tag that we discussed above.
#4. Not Mobile Friendly
Google introduced mobile-first indexing and this officially means the era of mobile is here and now.

Mobile-first indexing means that crawlers will first visit and rank the mobile version of your store and then will proceed to the desktop one. The reason for that is the increased amount of users accessing the content and websites via their mobile devices. So if you have not optimized your store yet, you may be in trouble.
Here are some of the recommendations for making the e-commerce store mobile friendly:
- Ensure that mobile and desktop sites have the same amount and quality of content. All elements – text, images, videos – should be in the required indexable formats for both mobile and desktop.
- Ensure both site versions contain metadata. Same as with content, the meta descriptions and titles should be the same for mobile and desktop.
- Pay attention to the proper use of robots.txt in both mobile and desktop.
- Shrink the titles, meta descriptions, and URLs. Because mobile devices have less screen space, it would be a good idea to optimize the content for the mobile. Just don’t sacrifice the keywords or important information here.
You can also read more on the official Google website.
#5. Slow Site Load Speed
If you thought page speed does not affect your ranking, unfortunately, you’ve been wrong. The average load time for a website is 3 seconds or less – so if your site does not load fast enough, you might be in trouble. By the way, you can check your site load speed here. PageSpeedInsights by Google analyze the site’s performance and speed and identify the main problem areas with alongside suggested recommendations for fixing them.
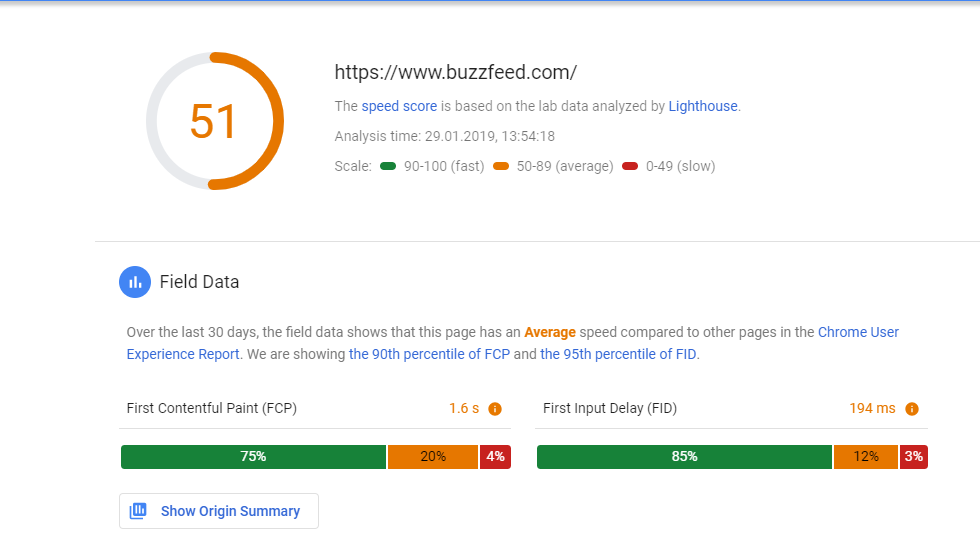
As well, slow speed affects conversions. Users do not have enough patience to wait for your store to load. As a result, they leave the site without proceeding to any conversion.
The general ways to solve these issues:
- Get rid of useless extensions and scripts;
- Optimize images;
- Improve your code, make it less bulky;
- Enable caching;
However, there are dozens of factors that impact the site load speed. As well, it depends on the platform on which your store is running. I.e., if your store is powered by Magento, you may want to check out this comprehensive speed guide.
Conclusion
The world of SEO is huge and the mistakes described above are only the top of an iceberg. If you suspect that your store needs a bit of an SEO, the best idea would be to consult with an SEO specialist and together develop a solid strategy to leverage the performance of your store. As well, it’s worth checking out this article on the Kaizen method for improving the SEO strategy and approaching it wisely.
Irina Linnik
Latest posts by Irina Linnik (see all)
- 5 On-Page SEO Mistakes Most E-commerce Website Owners Make - February 8, 2019






Thank you
Good Post its Very help full for me. i Read your Blog every day.Please write more about this topics.